by Dave Finnerty | Aug 11, 2024 | Best Practices, Education
 SIEM vs. SOAR vs. XDR:
SIEM vs. SOAR vs. XDR:

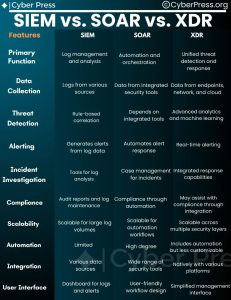
Understanding the Key Differences and How They Work Together in today’s rapidly evolving cybersecurity landscape, organizations need robust tools to detect, respond to, and mitigate threats. Three of the most significant technologies in this space are SIEM, SOAR, and XDR. While each serves a unique purpose, they often complement each other in creating a more secure environment.1. SIEM (Security Information and Event Management)Primary Function: SIEM solutions are designed to collect, analyze, and correlate security events and log data from various sources within an organization’s IT infrastructure. They provide real-time visibility into potential security incidents and help identify patterns that could indicate a threat.Example Products:SplunkIBM QRadarArcSightHow It Works: SIEM systems aggregate data from firewalls, antivirus programs, servers, applications, and other devices, then analyze this data for unusual patterns or anomalies. The system generates alerts that security teams can investigate further. SIEM is particularly useful for compliance reporting and providing a centralized view of security events across an organization.2. SOAR (Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response)Primary Function: SOAR platforms are designed to automate and coordinate security operations processes, helping security teams manage and respond to incidents more effectively and efficiently. These tools reduce the manual effort involved in responding to threats, allowing teams to focus on more complex tasks.Example Products:Palo Alto Networks Cortex XSOARSplunk SOAR (formerly Phantom)IBM ResilientHow It Works: SOAR platforms integrate with various security tools (including SIEMs) and automate workflows for incident response. For example, when a SIEM generates an alert, a SOAR platform can automatically trigger a predefined response action, such as isolating a compromised device or blocking malicious IP addresses. SOAR solutions also provide case management, threat intelligence, and collaboration tools, enhancing the overall effectiveness of security operations.3. XDR (Extended Detection and Response)Primary Function: XDR is an advanced security solution that goes beyond traditional endpoint detection and response (EDR) by integrating data from multiple security layers—such as endpoint, network, and email—to provide a unified and comprehensive threat detection and response platform.Example Products:Palo Alto Networks Cortex XDRTrend Micro XDRMicrosoft Defender XDRHow It Works: XDR solutions collect and correlate data from various security tools across the entire environment, providing deeper visibility and more accurate threat detection. By breaking down silos between different security layers, XDR offers a more holistic view of security incidents and automates response actions across all affected systems. This integration leads to faster detection and more coordinated responses to threats.Key Differences:SIEM focuses on log aggregation and analysis to identify potential security incidents and is widely used for compliance and reporting.SOAR emphasizes automation and orchestration of security operations, helping teams respond to incidents faster and with fewer manual processes.XDR provides comprehensive detection and response across multiple security layers, offering a more integrated approach to threat management compared to traditional EDR solutions.How They Work Together:SIEM can be used to feed data into SOAR platforms, which then automate the response to the alerts generated by the SIEM. This combination improves the speed and efficiency of threat response.XDR solutions can complement SIEM by providing more context and correlation across different security layers, enhancing the detection capabilities. When integrated with a SOAR platform, XDR can automate responses based on enriched data, creating a powerful defense mechanism.In summary, while SIEM, SOAR, and XDR serve distinct functions, they are most effective when used together. SIEM provides the visibility, SOAR automates the response, and XDR offers an integrated, context-rich threat detection capability. By combining these technologies, organizations can significantly enhance their security posture and respond more effectively to the ever-growing landscape of cyber threats

by Dave Finnerty | Jul 26, 2024 | Best Practices, Education

Top Three Cybersecurity Best Practices References
1. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Cybersecurity Framework
- Reputation: Highly respected and widely adopted within the industry, particularly in the United States. NIST is a federal agency known for its comprehensive and authoritative standards.
- Information Content: The framework provides a robust structure for managing and reducing cybersecurity risk. It includes detailed guidelines for identifying, protecting, detecting, responding to, and recovering from cyber incidents.
- URL: NIST Cybersecurity Framework
2. Center for Internet Security (CIS) Controls
- Reputation: Recognized globally for its practical and actionable cybersecurity guidelines. CIS Controls are developed by a community of cybersecurity experts and are used by organizations of all sizes.
- Information Content: The CIS Controls provide a prioritized set of actions to improve cybersecurity posture, focusing on practical steps to defend against the most common and significant cyber threats.
- URL: CIS Controls
3. ISO/IEC 27001:2013 – Information Security Management
- Reputation: Internationally recognized standard for information security management systems (ISMS). ISO/IEC 27001 is endorsed by many governments and industries around the world.
- Information Content: This standard provides comprehensive requirements for establishing, implementing, maintaining, and continually improving an ISMS. It covers various aspects of information security, including risk management and security controls.
- URL: ISO/IEC 27001:2013
These three references are highly regarded in the cybersecurity community for their depth of information and practical guidance on implementing effective cybersecurity measures. They offer extensive frameworks and controls that can be tailored to various organizational needs, making them invaluable resources for enhancing corporate cybersecurity.

by Dave Finnerty | Jul 25, 2024 | Best Practices, Education, Threats


Navigating Insider Risks: Are Your Employees Enabling External Threats?
Insider risks can arise from both malicious and accidental actions by employees. Accidental insiders often compromise security due to a lack of awareness, pressure to perform, poor credential handling, and unauthorized data movement. These actions can lead to significant financial, reputational, and operational damage. To mitigate these risks, companies should implement security awareness training, foster a security-conscious culture, monitor user activity, and institutionalize best practices.
For more details, visit The Hacker News.
Stay secure, everyone!

by Dave Finnerty | Jul 25, 2024 | Best Practices, Education, Tools


Friendly Summary by TheMadAdmin (AKA Dave)
6 Types of Application Security Testing You Must Know About
Application security testing is essential for developing secure software. Here are six key types:
- Penetration Testing for the SDLC: Identifies vulnerabilities throughout development stages.
- Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST): Tests running applications for runtime vulnerabilities.
- Static Application Security Testing (SAST): Analyzes source code for security flaws.
- Interactive Application Security Testing (IAST): Combines SAST and DAST for comprehensive testing.
- Fuzz Testing for APIs: Sends unexpected inputs to find vulnerabilities.
- Application Security Posture Management (APSM): Continuously manages application security.
For more details, read the full article on The Hacker News.
Stay secure, everyone!

by Dave Finnerty | Jul 25, 2024 | Best Practices, Education

Incident Response Cheat Sheet
Incident Response Cheat Sheet by TheMadAdmin (AKA Dave)
Step 1: Don’t Panic
- Stay calm and adopt a problem-solving attitude. This will help you and your team respond logically and effectively to the breach.
Step 2: Do Not Pay a Ransom
- Paying ransom often leads to more trouble. Invest in an Endpoint Detection and Response solution to handle ransomware before it executes.
Step 3: Form a Response Team
- Assemble a capable response team including IT staff, HR, and PR. They will investigate, address the breach, and manage communications.
Step 4: Use Backup Servers
- If available, switch to backup servers to maintain operations. Ensure your backups are tested regularly.
Step 5: Isolate the Breach
- Minimize the number of affected systems by isolating the breached area. Test other network segments to ensure they are secure.
Step 6: Investigate & Manage
- Investigate the breach to understand the damage. Address any impacts, especially on employees and your company’s reputation.
Step 7: Document
- Document the breach and your response thoroughly. This helps in refining your response strategy and future prevention.
Step 8: Contact Clients
- Notify affected clients promptly and provide them with necessary information, especially if their private data was compromised.
Step 9: Prevent Future Attacks
- Consider partnering with an external cybersecurity firm if your team struggles with securing your IT infrastructure. Managed Security Services Providers (MSSPs) can be more efficient.
Important Contact Information:
- IT Contact: For remediation efforts
- Legal Counsel: For breach notification and reporting
- PR Contact: For client notifications
- HR Contact: For employee impacts
- Local Law Enforcement: May be needed for insurance claims
- FBI Field Office: www.fbi.gov – Report cyber crimes
Why You Need an Incident Response Policy
Having a written Incident Response policy is crucial as it ensures your organization is prepared for cybersecurity incidents. This policy:
- Provides clear steps to manage and mitigate breaches, minimizing damage.
- Ensures all team members understand their roles and responsibilities.
- Helps maintain client trust by demonstrating a proactive approach to security.
- Assists in regulatory compliance and reduces potential legal liabilities.
Prepared by: TheMadAdmin (AKA Dave)
Having a well-documented policy helps your team stay organized and effective during a crisis, ensuring a swift and controlled response.
by tma | Jul 4, 2024 | Best Practices
Best Practice Post Best Practice Post Best Practice Post Best Practice Post Best Practice Post Best Practice Post Best Practice Post Best Practice Post Best Practice Post Best Practice Post Best Practice Post Best Practice Post Best Practice Post Best Practice Post Best Practice Post Best Practice Post Best Practice Post Best Practice Post Best Practice Post Best Practice Post Best Practice Post Best Practice Post Best Practice Post Best Practice Post Best Practice Post Best Practice Post Best Practice Post Best Practice Post Best Practice Post Best Practice Post Best Practice Post Best Practice Post Best Practice Post Best Practice Post Best Practice Post Best Practice Post Best Practice Post Best Practice Post Best Practice Post Best Practice Post Best Practice Post Best Practice Post Best Practice Post Best Practice Post Best Practice Post Best Practice Post Best Practice Post Best Practice Post Best Practice Post Best Practice Post Best Practice Post Best Practice Post Best Practice Post Best Practice Post Best Practice Post Best Practice Post





